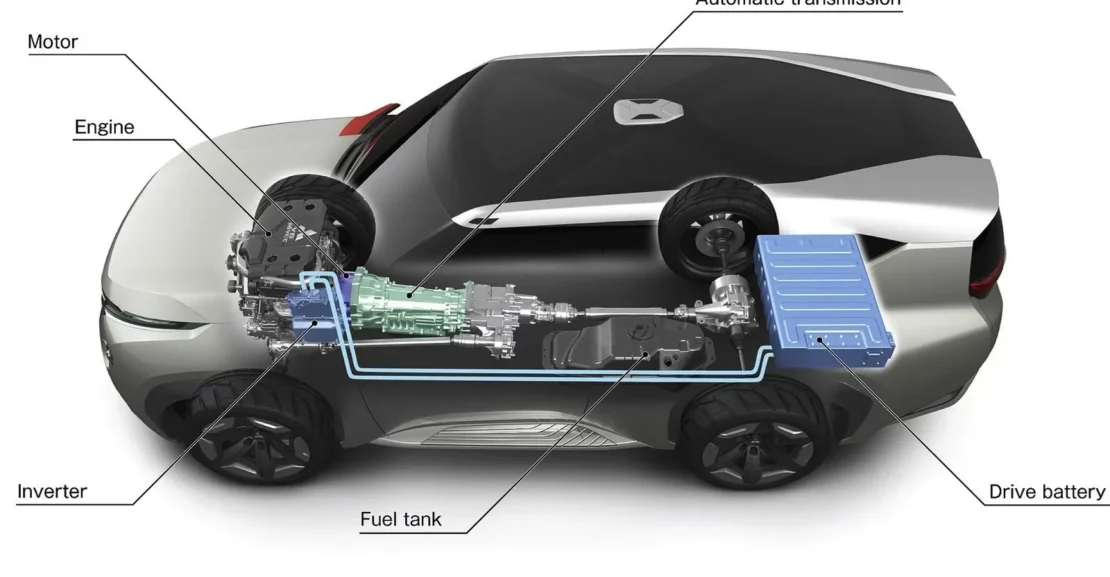
Ever wondered how electric cars actually work? What keeps electric vehicles moving and why is electric vehicle technology taking over the world? This guide breaks it all down — from electric motors to batteries to the science behind electric vehicles charging — in a way that’s easy, friendly, and totally free of complicated tech talk.
Source: https://evse.com.au/blog/how-does-an-electric-car-work/
Introduction: A New Era of Driving — Step Into the World of Electric Vehicles
Ever wondered about the buzz around electric cars and how they actually function? It’s hard to miss how rapidly they’re taking over the roads.
From Tesla’s head-turning designs to the smaller electric vehicles buzzing around busy streets, electric cars are flipping the whole idea of driving on its head.
But what’s really happening under the hood? And why are electric vehicles so different from the cars we were used to?
Let’s examine electric vehicle technology — explained so simply, you can chat about it with a friend. Using no heavy jargon here!
How do Electric Vehicles Work and How Are They Different From Other Cars?
Before we dive into the mechanism of action of electric vehicles, let’s get to know the basics of these cars.
Energy from the electric battery gets stored and fed straight to the electric motors which keeps the wheels turning and keeps the ride smooth.
Unlike traditional gas cars — packed with complicated engines and endless moving parts — electric vehicles keep things way simpler, smarter, and a whole lot more efficient.
Electric cars are smarter, simpler and more efficient when it comes to comparing them with gas powered vehicles which not only have their complicated engines but also contain 100s of moving parts in them.
Major differences at a glance:
- Electric vehicles are quieter
- Electric vehicles emit zero tailpipe emissions
- Electric vehicles have fewer parts to maintain
- Electric vehicles offer instant torque (meaning faster acceleration)
The Heart of an Electric Car: Understanding Electric Motors
At the center of every electric vehicle is an electric motor.
You can think of it as the “engine” of an electric vehicle — but much simpler and smarter.
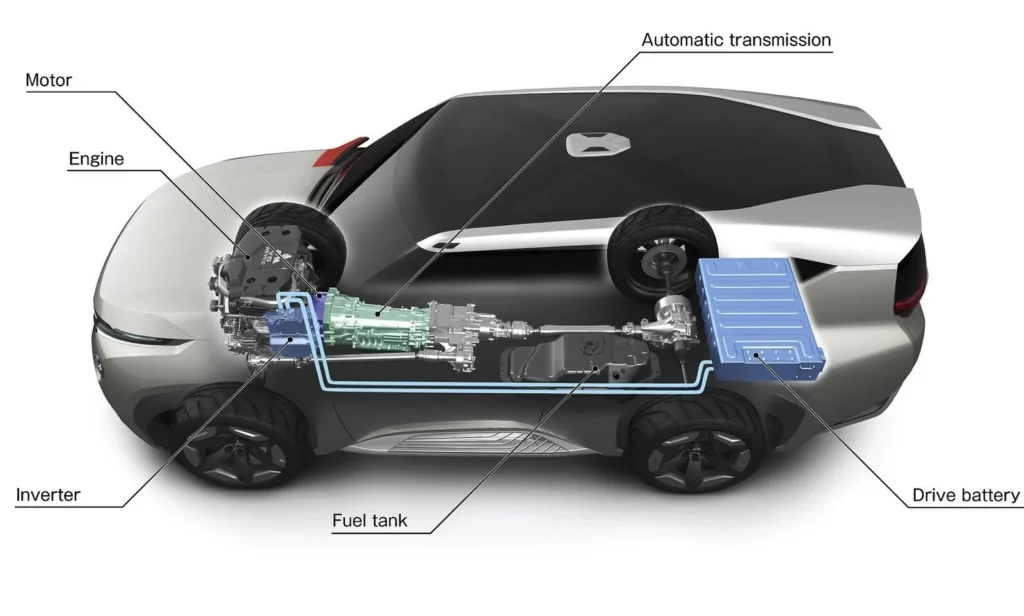
How Electric Motors Work in Electric Vehicles
Source: https://www.power-sonic.com/blog/types-of-electric-vehicles/
- Energy Transfer:
As soon as you hit the accelerator, an electric current is sent straight to the core- the motor, bringing the vehicle to life and getting it ready to function.
- Active Magnetic Fields:
Within the motor are magnets creating magnetic fields. The magnetic field lines generated by the magnetic field cause the rotor to spin and hence turn the wheels. No fuel burning, no noisy ignition, no gear shifting. Just a quiet and smooth experience.
- Regen Braking:
A very smart thing about electric vehicles is their regenerative braking.
Normally, when we hit the brakes, the heat produced as a result is wasted into the environment, however, in electric vehicles, the story is far better and more interesting. Electric vehicle braking technology doesn’t let any heat go to waste, it brings the heat energy into use by converting it into electric energy ready for its storage in the battery. Now, even the need to charge frequently has decreased.
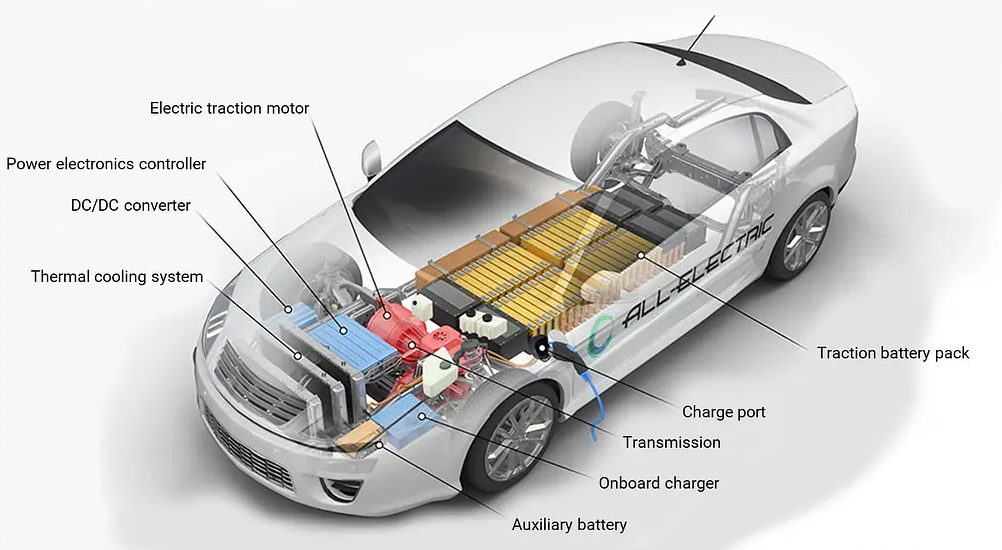
The EV Battery Pack: Fueling the Future
Electric motor – the heart. Battery pack – the soul.
Different types of batteries used in electric vehicles
The widely used batteries in electric vehicles are the same that are used in your smartphone, smart watches and even solar panels.. These are Lithium-ion batteries. EVs use the same lithium ion batteries but on a bigger and more powerful scale.
Other types include:
- Solid-state batteries (emerging technology — safer, faster-charging)
Solid-state batteries are safer because they use solid electrolytes instead of flammable liquids, reducing the risk of fires and leaks. They also charge faster and offer greater energy efficiency, making them ideal for next-gen EVs. - Nickel-metal hydride (used in hybrids like Toyota Prius)
How Electric Vehicle Batteries Work
1) Charging:
You plug the electric vehicles into a charger, and electricity flows into the battery.
2) Storing Energy:
The battery stores this electrical energy chemically.
3) Supplying Energy:
When needed, it releases the electricity to power the motor.
The manufacturer is the one controlling the size, capacity and weight of the battery according to the vehicle type.
Electric Vehicle Charging Made Simple: From Home Setups to Lightning-Fast Networks
Electric cars charging at home:
Convenient And Always Ready
Electric vehicle owners mostly opt for Level 2 charging at home because of the voltage (240V) used in charging. These cars have batteries similar to the ones used in bigger appliances such as a dryer. It’s like sending your car in your charger-installed garage for a good night’s sleep only to wake it up fresh and fully energized.
Electric cars public charging stations:
Growing Everywhere
If you’re in a rush and have only 20-30 minutes for recharging, fast chargers (DC fast chargers) are your best friends which can charge your car’s battery up to 80%.
Electric companies like Tesla Supercharger, ChargePoint and ElectrifyAmerica are establishing fast charging stations across highways, malls and big cities , for the convenience of EV users.
Search tip:
If you’re looking for a charging station, search “Electric vehicles charging station near me” — get the fastest results every time!
Power Electronics: The Silent Workers in Electric Vehicles
You don’t see them, but power electronics work quietly to manage everything within electric cars.These are sophisticated electronic systems made up of components like inverters, converters, and controllers that regulate and direct the flow of electrical energy.
- They control how much energy flows from the battery to the motor.
- They convert AC to DC or DC to AC depending on what’s needed.
- They ensure smooth acceleration and deceleration.
Without these little geniuses, electric vehicles wouldn’t feel nearly as zippy or efficient.
How Do Electric Cars Start and Move?
- You press the start button.
- Battery sends electricity to the motor.
- Motor turns the wheels.
- As you drive, the electronics manage power flow and regenerative braking.
- When you stop or slow down, energy is saved and reused!
Simple, clean, efficient — that’s the magic of electric vehicles.
Fun fact:
In many modern electric vehicles, you can almost drive with just one pedal — lift your foot to slow down and recharge!
Electric vehicle driving experience: Instant torque and smooth ride
In plain English:
- Step on the pedal → Immediate zoom!
- No engine revving, no gear shifting delays.
This is why even compact electric vehicles feel surprisingly powerful when you drive them.
This makes the electric vehicles fun to drive even on rainy days!
Why Electric Vehicles Are More Efficient Than Gas Cars
Oil/gas engines consume a lot of energy and waste heat.
Electric motors, on the other hand, convert over 85% of the battery’s energy into kinetic energy – motion.
Result?
- Longer driving range
- Lower operating costs
- Less environmental impact
Common Myths About How Electric Cars Work (Debunked!)
- Myth: Electric vehicles are slower than gasoline cars.
Truth: Many electric vehicles are faster in acceleration because of instant torque. - Myth: Batteries need frequent replacement.
Truth: Modern electric vehicles batteries can last 8–15 years or longer. - Myth: Electric vehicles can’t drive long distances.
Truth: With ranges of 300–500+ km, most electric vehicles easily cover daily needs — and charging networks are growing fast.
Are Electric Vehicles the Future of Transportation?
All signs point to yes.
Countries like Norway, Germany, China, and even the USA are heavily investing in electric vehicles technology.
Car manufacturers are introducing more models each year — SUVs, sedans, trucks, you name it!
Reasons for why electric vehicles are here to stay for longer:
- Better battery technology
- Lower production costs, leading to more affordable prices for consumers
- Government incentives
- Global focus on reducing carbon emissions
Quick Glossary of Electric Car Terms You Should Know
BEV – Battery electric vehicle
PHEV – Plug-in Hybrid electric vehicle
kWh – Kilowatt-hour (battery capacity)
Regenerative braking – Capturing braking energy
Charging station – Place to charge electric vehicles
Conclusion: The Electrifying Journey Ahead
So, how do electric cars work?
In short: cleanly, efficiently, and smartly.
An electric car isn’t just another vehicle — it’s a whole new experience in how we drive, own, and look after our cars.
As batteries get smarter, charging speeds up, and prices keep falling, electric vehicles won’t be something we’ll wait for in the future — they’ll be parked in every driveway before we know it.
So next time someone asks, “How do electric cars actually work?” — you’ll be ready with a simple, clear answer that makes you sound like a total pro.
Thinking About Taking the Leap into the Electric World?
Whether you’re just starting to think about switching to an electric vehicle, planning your own charging setup at home, or simply curious about cleaner tech, there’s honestly never been a better time.
The world is shifting to electric — and the ride ahead looks smoother, cleaner, and a lot more exciting!
Citations
- EVSE Australia. (n.d.). How does an electric car work? EVSE. Retrieved from https://evse.com.au/blog/how-does-an-electric-car-work/
- Power Sonic Corporation. (n.d.). Types of electric vehicles. Retrieved from https://www.power-sonic.com/blog/types-of-electric-vehicles/
- U.S. Department of Energy. (n.d.). Electric vehicle basics. Alternative Fuels Data Center. Retrieved from https://afdc.energy.gov/vehicles/electric_basics_ev.html
- International Energy Agency. (2023). Global EV Outlook 2023. Retrieved from https://www.iea.org/reports/global-ev-outlook-2023
- Tesla, Inc. (n.d.). Supercharging. Retrieved from https://www.tesla.com/supercharger
- ChargePoint. (n.d.). How EV charging works. Retrieved from https://www.chargepoint.com/
- Electrify America. (n.d.). Our network. Retrieved from https://www.electrifyamerica.com/